Configuration#
time expected: 11 minutes
BentoML provides a configuration interface that allows you to customize the runtime behaviour of your BentoService. This article highlight and consolidates the configuration fields definition, as well as some of recommendation for best-practice when configuring your BentoML.
Configuration is best used for scenarios where the customizations can be specified once and applied anywhere among your organization using BentoML.
BentoML comes with out-of-the-box configuration that should work for most use cases.
However, for more advanced users who wants to fine-tune the feature suites BentoML has to offer,
users can configure such runtime variables and settings via a configuration file, often referred to as
bentoml_configuration.yaml.
Note
This is not to be mistaken with the bentofile.yaml which is used to define and
package your Bentos.
This configuration file are for BentoML runtime configuration.
Providing configuration during serve runtime#
BentoML configuration is a YAML file which can then be specified via the environment variable BENTOML_CONFIG.
For example, given the following bentoml_configuration.yaml that specify that the
server should only use 4 workers:
version: 1
api_server:
workers: 4
Said configuration then can be parsed to bentoml serve like below:
» BENTOML_CONFIG=~/bentoml_configuration.yaml bentoml serve iris_classifier:latest
Note
Users will only have to specify a partial configuration with properties they wish to customize. BentoML will then fill in the rest of the configuration with the default values [2].
In the example above, the number of API workers count is overridden to 4. Remaining properties will take their defaults values.
Variables in the form of ${ENV_VAR} will be expanded at runtime to the value of the corresponding environment variable, but please note that this only supports string types.
For example:
ssl:
keyfile_password: ${MY_SSL_KEYFILE_PASSWORD}
In addition, you can provide default values that will take effect when the environment variable is not set in the following form:
ssl:
keyfile_password: ${MY_SSL_KEYFILE_PASSWORD:-default_value}
See also
Overriding configuration with environment variables#
Users can also override configuration fields with environment variables. by defining
an oneline value of a “flat” JSON via BENTOML_CONFIG_OPTIONS:
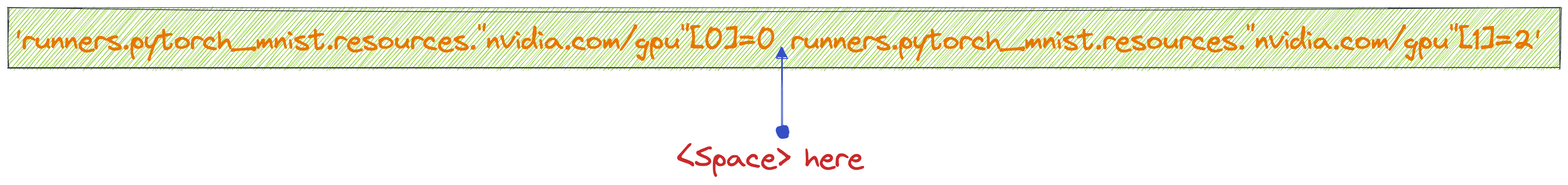
$ BENTOML_CONFIG_OPTIONS='runners.pytorch_mnist.resources."nvidia.com/gpu"[0]=0 runners.pytorch_mnist.resources."nvidia.com/gpu"[1]=2' \
bentoml serve pytorch_mnist_demo:latest
Which the override configuration will be intepreted as:
runners:
pytorch_mnist:
resources:
nvidia.com/gpu: [0, 2]
Note
For fields that represents a iterable type, the override array must have a space separating each element:
Mounting configuration to containerized Bento#
To mount a configuration file to a containerized BentoService, user can use the
-v option to mount the configuration file to the container and
-e option to set the BENTOML_CONFIG environment variable:
$ docker run --rm -v /path/to/configuration.yml:/home/bentoml/configuration.yml \
-e BENTOML_CONFIG=/home/bentoml/configuration.yml \
iris_classifier:6otbsmxzq6lwbgxi serve
Voila! You have successfully mounted a configuration file to your containerized BentoService.
Configuration fields#
On the top level, BentoML configuration [2] has three fields:
version: The version of the configuration file. This is used to determine the compatibility of the configuration file with the current BentoML version.api_server: Configuration for BentoML API server.runners[4]: Configuration for BentoService runners.
version#
BentoML configuration provides a version field, which enables users to easily specify
and upgrade their configuration file as BentoML evolves.
This field will follow BentoML major version number. For every patch releases that introduces new configuration fields, a compatibility layer will be provided to ensure there is no breaking changes.
Note that
versionis not a required field, and BentoML will default to version 1 if it is not specified.However, we encourage users to always version their BentoML configuration.
api_server#
The following options are available for the api_server section:
Option |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
|
Number of API workers for to spawn |
null [1] |
|
Traffic control for API server |
See traffic |
|
Maximum number of connections to hold in backlog |
2048 |
|
Key and values to enable metrics feature |
See metrics |
|
Key and values to enable logging feature |
|
|
Key and values to configure HTTP API server |
See http |
|
Key and values to configure gRPC API server |
See grpc |
|
Key and values to configure SSL |
See ssl |
|
Key and values to configure tracing exporter for API server |
See Tracing |
traffic#
You can control the traffic of the API server by setting the traffic field.
To set the maximum number of seconds to wait before a response is received, set api_server.traffic.timeout, the default value is ``60``s:
api_server:
traffic:
timeout: 120
To set the maximum number of requests in the process queue across all runners, set api_server.traffic.max_concurrency, the default value is infinite:
api_server:
traffic:
max_concurrency: 50
metrics#
BentoML utilises Prometheus to collect metrics from the API server. By default, this feature is enabled.
To disable this feature, set api_server.metrics.enabled to false:
api_server:
metrics:
enabled: false
Following labeling convention set by Prometheus, metrics generated
by BentoML API server components will have namespace bentoml_api_server, which can
also be overridden by setting api_server.metrics.namespace:
api_server:
metrics:
namespace: custom_namespace
Note: for most use cases, users should not need to change the default
namespacevalue.
There are three types of metrics every BentoML API server will generate:
request_duration_seconds: This is a Histogram that measures the HTTP request duration in seconds.There are two ways for users to customize duration bucket size for this metrics:
Provides a manual bucket steps via
api_server.metrics.duration.buckets:api_server: metrics: duration: buckets: [0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10]
Automatically generate an exponential buckets with any given
min,maxandfactor:api_server: metrics: duration: min: 0.1 max: 10 factor: 1.2
Note
duration.min,duration.maxandduration.factorare mutually exclusive withduration.buckets.duration.factormust be greater than 1.
By default, BentoML will respect the default duration buckets provided by Prometheus.
request_total: This is a Counter that measures the total number of HTTP requests.request_in_progress: This is a Gauge that measures the number of HTTP requests in progress.
The following options are available for the metrics section:
Option |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
|
Enable metrics feature |
|
|
Namespace for metrics |
|
|
Duration buckets for Histogram |
Prometheus bucket value [3] |
|
factor for exponential buckets |
null |
|
upper bound for exponential buckets |
null |
|
lower bound for exponential buckets |
null |
http#
Configuration under api_server.http will be used to configure the HTTP API server.
By default, BentoML will start an HTTP API server on port 3000. To change the port, set api_server.http.port:
api_server:
http:
port: 5000
Users can also configure CORS via api_server.http.cors. By default CORS is disabled.
If specified, all fields under api_server.http.cors will then be parsed to CORSMiddleware:
api_server:
http:
cors:
enabled: true
access_control_allow_origins: ["http://myorg.com:8080", "https://myorg.com:8080"]
access_control_allow_methods: ["GET", "OPTIONS", "POST", "HEAD", "PUT"]
access_control_allow_credentials: true
access_control_allow_headers: ["*"]
access_control_allow_origin_regex: 'https://.*\.my_org\.com'
access_control_max_age: 1200
access_control_expose_headers: ["Content-Length"]
Deprecated since version 1.0.16: access_control_allow_origin is deprecated. Use access_control_allow_origins instead.
grpc#
This section will go through configuration that is not yet coverred in our guides on performance tuning.
Similar to HTTP API server, BentoML will start a gRPC API server on port 3000 by default. To change the port, set api_server.grpc.port:
api_server:
grpc:
port: 5000
Note that when using bentoml serve-grpc and metrics is
enabled, a Prometheus metrics server will be started as a sidecar on port 3001. To change the port, set api_server.grpc.metrics.port:
api_server:
grpc:
metrics:
port: 50051
By default, the gRPC API server will disable reflection. To always enable server reflection,
set api_server.grpc.reflection.enabled to true:
api_server:
grpc:
reflection:
enabled: true
Note
User can already enable reflection by passing --enable-reflection to bentoml serve-grpc CLI command.
However, we also provide this option in the config file to make it easier for users who wish to always enable reflection.
ssl#
BentoML supports SSL/TLS for both HTTP and gRPC API server. To enable SSL/TLS, set api_server.ssl.enabled to true:
api_server:
ssl:
enabled: true
When using HTTP API server, BentoML will parse all of the available fields directly to Uvicorn.
Todo
Add instruction how one can setup SSL for gRPC API server.
Notes