Manage access tokens#
In BentoCloud, API tokens serve as a key method of authorization for two distinct scopes - BentoCloud resources and Bento Deployments. They correspond to two different types of tokens - User tokens and Developer tokens.
User tokens are granted permissions to access deployed Bento applications. You can control access to Bento Deployments with the following endpoint access types.
Protected: The Deployment is accessible to anyone on the internet, provided that they have a valid token.
Public: The Deployment is accessible to anyone on the internet.
Note
You can specify the endpoint access type when creating and updating a Deployment.
Developer tokens are granted permissions to manage BentoCloud resources. For example, you can perform the following tasks with a Developer token:
Manage BentoCloud cluster configurations.
Handle identity and access management (IAM) policies.
Manage models, Bentos, and Deployments.
This tutorial explains how to create and use API tokens in BentoCloud.
Create an API token#
To create an API token, perform the following steps:
Navigate to the API Tokens page in the BentoCloud Console.
Click Create.
In the dialog that appears, specify the following fields. Note that you must select at least one of the token types.
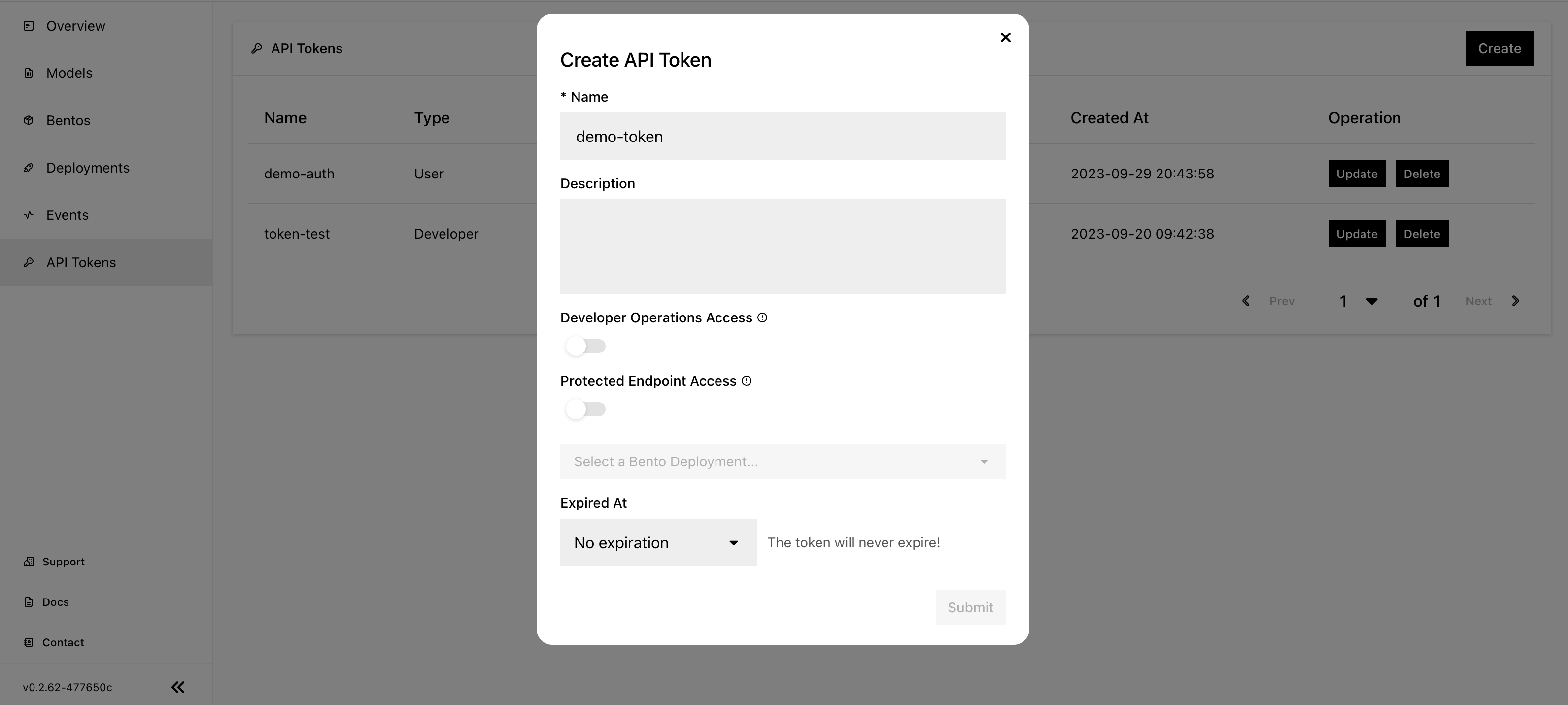
Name: The name of the API token.
Description: A description of the token, detailing its usage.
Developer Operations Access (Developer token): Grant permissions to access BentoCloud and manage resources on it.
Protected Endpoint Access (User token): Grant permissions to access Bento Deployments with Protected endpoints. If you select this token type, you need to choose the Deployment that you want the token to access. If you want to use the token to access all the Protected Deployments, select All Deployments.
Expired At: Set an expiration date for the token. You won’t be able to use the token after it expires.
Click Submit.
Record the token. This is the only opportunity to record it.
All available tokens appear on the API Tokens page. Click Delete if you no longer needs a token.
Use the Developer token#
Interact with BentoCloud programmatically via the BentoML Command Line Interface (CLI). Log in using the following command.
bentoml cloud login --api-token <your-api-token> --endpoint <your-bentocloud-endpoint>
Note
You should see the above command after you create a token.
Expected output:
Successfully logged in as user "user" in organization "mybentocloud".
To retrieve the current endpoint and API token locally, make sure you have installed jq, and then run:
bentoml cloud current-context | jq '("endpoint:" + .endpoint + ", api_token:" + .api_token)'
After you log in, you should be able to manage BentoCloud resources. For more information on the CLI, see Reference - CLI.
Use the User token#
You can use User tokens to access Protected Bento Deployments.
For HTTP-based servers, include the token in the header of your HTTP request.
curl "http://app-name.organization.cloud-apps.bentoml.com" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_TOKEN" \
--data '{"prompt": "What state is Los Angeles in?", "llm_config": {"max_new_tokens": 129}}'
To access a Protected Deployment from a web browser, you can add the token in the header using any browser extension that supports this feature, such as Header Inject in Google Chrome.
Create a User token by following the steps in the Create an API token section above. Make sure you select the desired Deployment that you want the token to access.
Install Header Inject in Google Chrome and enable it.
Select Header Inject, click Add, and specify Header name and Header value.
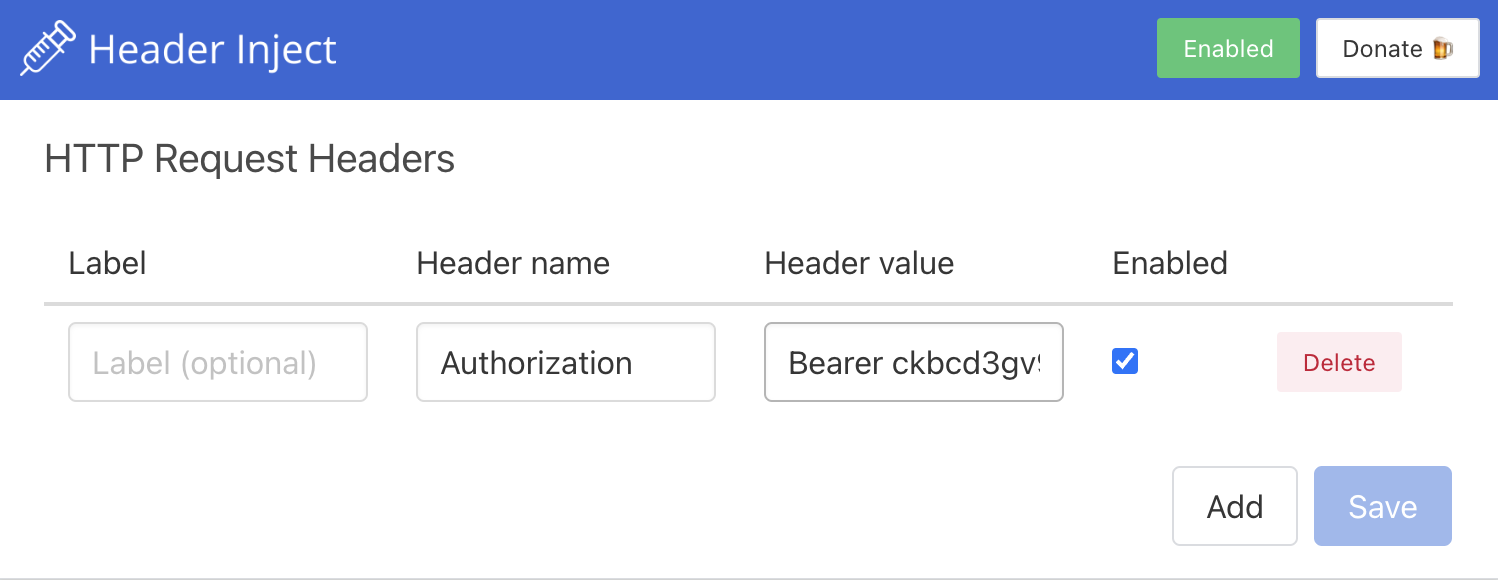
Header name: Enter
Authorization.Header value: Enter
Bearer $YOUR_TOKEN.
Click Save.
Access the exposed URL of your Protected Deployment again and you should be able to access it.
For gRPC servers, include it in the metadata of your gRPC call:
import grpc
creds = grpc.ssl_channel_credentials()
auth_creds = grpc.access_token_call_credentials('<your-api-token>')
channel = grpc.secure_channel('<your-deployed-api-endpoint>', creds)
stub = <YourGRPCServiceStub>(channel)